
Sustainable nutrition is ensuring wholesome, nutrient-dense foods are accessible, affordable and culturally relevant while also preserving environmental resources and supporting local communities.1 Dairy plays an important role in sustainable nutrition through health and nutrition, culture and community, environment and the economy.

 Milk
provides a balanced contribution of fat, protein and carbohydrates, impacting how its rich nutrient package is absorbed and used in the body throughout the day to support a healthy lifestyle.
Milk
provides a balanced contribution of fat, protein and carbohydrates, impacting how its rich nutrient package is absorbed and used in the body throughout the day to support a healthy lifestyle.


 California
is making significant investments to improve school meals through Farm-to-School programming that purchases food from local farms, offers students food education and provides hands-on learning that supports students’ academic achievement,
health and well-being.13
California
is making significant investments to improve school meals through Farm-to-School programming that purchases food from local farms, offers students food education and provides hands-on learning that supports students’ academic achievement,
health and well-being.13
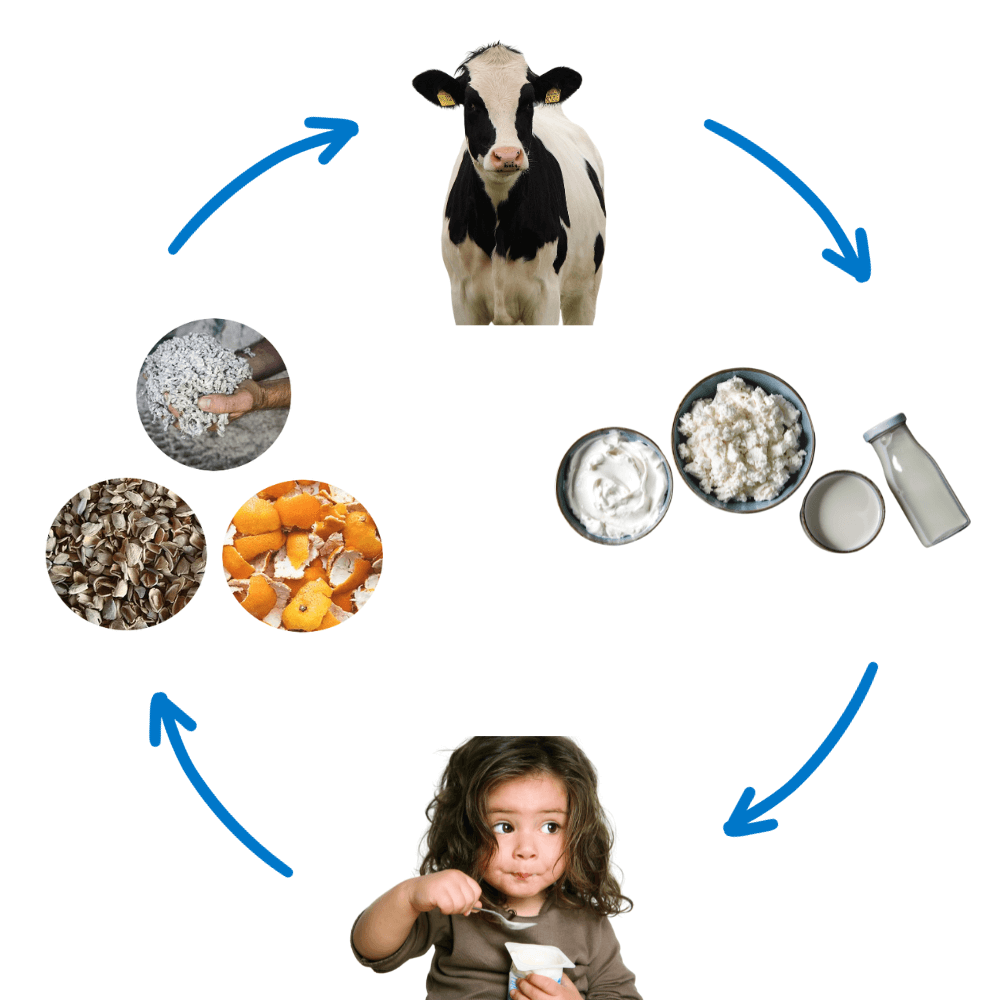



 Sustainable
nutrition is a complex topic, as countries around the world are faced with addressing malnutrition, obesity and micronutrient deficiencies20 while protecting finite natural resources. Here in California, advances in technology and agricultural innovation
can support sustainable food systems that provide nutrient-dense plant and animal source foods to ensure nutrition security and optimal health for all.
Sustainable
nutrition is a complex topic, as countries around the world are faced with addressing malnutrition, obesity and micronutrient deficiencies20 while protecting finite natural resources. Here in California, advances in technology and agricultural innovation
can support sustainable food systems that provide nutrient-dense plant and animal source foods to ensure nutrition security and optimal health for all.
References
1. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization. Sustainable Healthy Diets: Guiding Principles. FAO and WHO; 2019. Accessed December 1, 2023. https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/ca6640en
2. Robertson RC, Manges AR, Finlay BB, Prendergast AJ. The human microbiome and child growth: first 1000 days and beyond. Trends in Microbiol . 2019;27(2):131-147. DOI:10.1016/j.tim.2018.09.008
3. Schwarzenberg SJ, Georgieff MK, Committee on Nutrition. Advocacy for improving nutrition in the first 1000 days to support childhood development and adult health. Pediatrics. 2018;141(2):e20173716. DOI:10.1542/peds.2017-3716
4. Lana A, Rodríguez-Artalejo F, López-García E. Dairy consumption and risk of frailty in older adults: A prospective cohort study. J Am Geriatr Soc.2015;9(63):1852–60.doi:10.1111/jgs.13626
5. Hidayat K, Du X, Shi B-M, Qin L-Q. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between dairy consumption and the risk of hip fracture: Critical interpretation of the currently available evidence. Osteoporos Int .2020;31(8):1411–1425.
DOI:10.1007/s00198-020-05383-3
6. Choi IY, Taylor MK, Lee P, et al. Milk intake enhances cerebral antioxidant (glutathione) concentration in older adults: a randomized controlled intervention study. Front Nutr. 2022;9. DOI:10.3389/fnut.2022.811650
7. Canipe LG, Sioda M, Cheatham CL. Diversity of the gut-microbiome related to cognitive behavioral outcomes in healthy older adults. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2023;96:104464. DOI:10.1016/j.archger.2021.104464
8. Mozaffarian D. Dairy foods, obesity, and metabolic health: The role of the food matrix compared with single nutrients. Adv Nutr. 2019;10(5):917S-923S. DOI:10.1093/advances/nmz053
9. Feng X, Zhao Y, Liu J, et al. Consumption of dairy products and the risk of overweight or obesity, hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A dose-response meta-analysis and systematic review of cohort studies. Adv Nutr. 2022;13(6):2165-2179. DOI:
10.1093/advances/nmac096
10. Ulven SM, Holven KB, Gil A, Rangel-Huerta OD. Milk and Dairy Product Consumption and Inflammatory Biomarkers: An Updated Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Adv Nutr. May 1 2019;10(suppl_2):S239-S250. DOI:10.1093/advances/nmy072
11. Nieman KM, Anderson BD, Cifelli CJ. The effects of dairy product and dairy protein intake on inflammation: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Coll Nutr. 2020;40(6):571-582. DOI:10.1080/07315724.2020.1800532
12. Hirst KK. Dairy farming the ancient history of producing milk. Updated May 30, 2019. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.thoughtco.com/dairy-farming-ancient-history-171199
13. Our values. National Farm to School Network; 2021. Accessed December 1, 2023. https://assets.website-files.com/5b88339c86d6045260c7ad87/613797bd05726e5c091c5280_OurValues.pdf
14. Planet-smart dairy. Dairy Cares website. Accessed December 1, 2023. https://www.dairycares.com/planet-smart-dairy
15. Kebreab E, Mitloehner F, Sumner DA. Meeting the Call: How California Is Pioneering a Pathway to Significant Dairy Sector Methane Reduction. UC Davis CLEAR Center; 2022. Accessed December 12, 2023. https://clear.ucdavis.edu/sites/g/files/dgvnsk7876/files/inline-files/Meeting-
the-Call-California-Pathway-to-Methane-Reduction.pdf
16. Capper JL, Cady RA. The effects of improved performance in the US dairy cattle industry on environmental impacts between 2007 and 2017. J Anim Sci. 2020;98(1):skz291. DOI:10.1093/jas/skz291
17. Dairy environmental sustainability. Dairy Management Inc website. Accessed December 1, 2023. https://www.usdairy.com/sustainability/environmental-sustainability
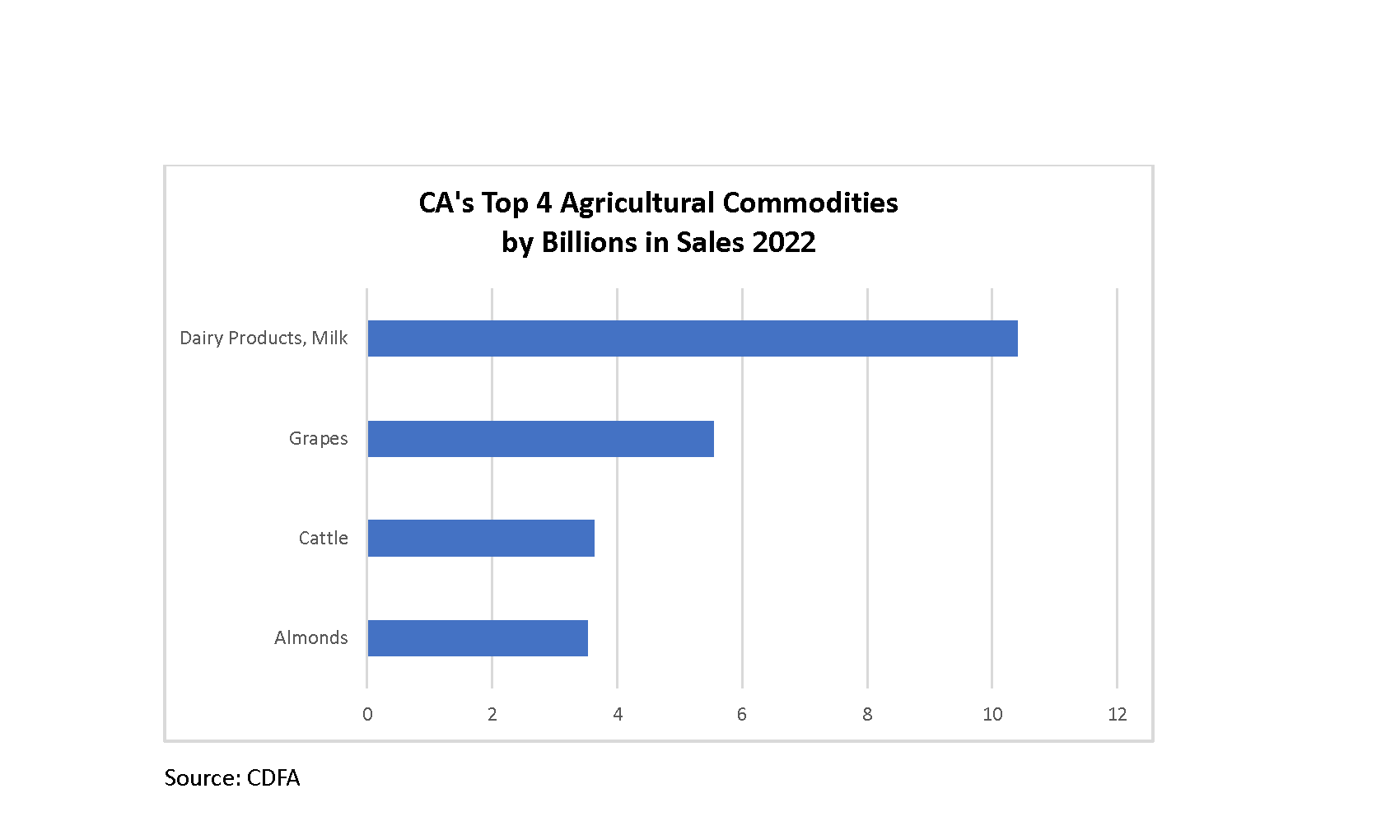
18. California Department of Food and Agriculture. California Agricultural Production Statistics. Updated August 31, 2023. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.cdfa.ca.gov/Statistics/
Issue 5: IDF Dairy Sustainability Outlook
Issue 7: IDF Dairy Sustainability Outlook - FAO Global Conference on Sustainable Livestock Transformation